Molecular dynamics study of grain boundaries and triple junctions in ice
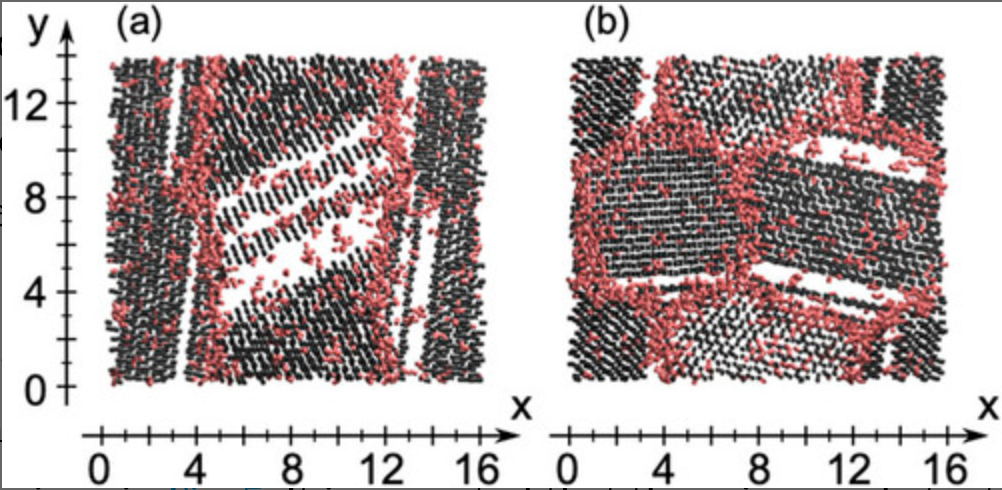
We perform classical molecular dynamics simulations of polycrystalline ice at 250 K using the TIP4P/Ice model. The structures of polycrystalline ice are prepared by growing ice particles in supercooled water. An order parameter developed recently is used to characterize local structures in terms of the liquid–liquid phase transition scenario. It is shown that the grain boundaries and triple junctions in ice are structurally similar to low-density liquid water in which most water molecules form four hydrogen bonds and the O–O–O angles deviate from the tetrahedral angle of 109.47°. The thickness of the grain boundaries is ∼1 nm. The diffusion coefficient of water molecules along the grain boundaries calculated in this study, 5.0 × 10−13 m2 s−1, is in good agreement with experimental data. The diffusion along the triple junctions is 3.4 times faster than that along the grain boundaries. We model the grain size dependence of diffusivity of water molecules in polycrystalline ice using the simulation results and find that the impact of the grain boundaries and the triple junctions on the diffusivity is negligible for typical polycrystalline ice samples having grain sizes of the order of millimeters. We also demonstrate that the properties of the grain boundaries are quite different from those of the ice/vapor interface at the same temperature: the quasi-liquid layer at the ice/vapor interface is similar to high-density liquid water and the diffusion coefficient along the ice/vapor interface is two orders of magnitude larger than that along the grain boundaries.
Takuma Yagasaki, Masakazu Matsumoto, and Hideki Tanaka, Molecular dynamics study of grain boundaries and triple junctions in ice, J. Chem. Phys. 153, 124502 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0021635]
