paper2024
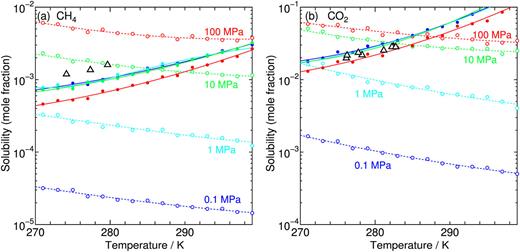
On the phase behaviors of CH4–CO2 binary clathrate hydrates`:` Equilibrium with aqueous phase
A new paper from our research group has been published. We explore the solubilities of guest CH4 and/or CO2 in the aqueous state coexisting with the corresponding hydrate. The equilibrium conditions are estimated by calculating the chemical potentials of water and guest species in the hydrate on the basis of a statistical mechanical theory using pairwise intermolecular potentials. This requires the least computational cost while covering a wide range of temperature, pressure, and composition of guest species, even for the binary hydrate.
Emergence of the pentagonal ice nanocrystal
A new paper from our research group has been published. Press Release (in Japanese) Multitwinned nanocrystals are commonly found in substances that preferentially adopt tetrahedral local arrangements, but not yet in water crystals. Ice nanocrystals are pivotal in cloud microphysics, and their surfaces become increasingly prominent in determining structure as crystal size decreases. Nevertheless, discussions on nanocrystal structures have predominantly centered on ice polymorphs observed in bulk: hexagonal (Ih), cubic (Ic), and stacking-disordered (Isd) ices.
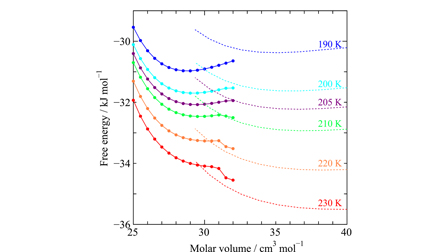
Stability mechanism of crystalline CO2 and Xe
A new paper from our research group has been published. We explore the phase behaviors of simple molecular crystals in order to investigate the molecular basis of the stability mechanism relative to their liquid counterparts. The free energies of the face centered cubic crystals of Xe and CO2 are calculated as a collection of oscillators, and those of the liquids are from an equation of state via molecular dynamics simulations. The vibrational free energy in the solid is separated into the harmonic and anharmonic terms.
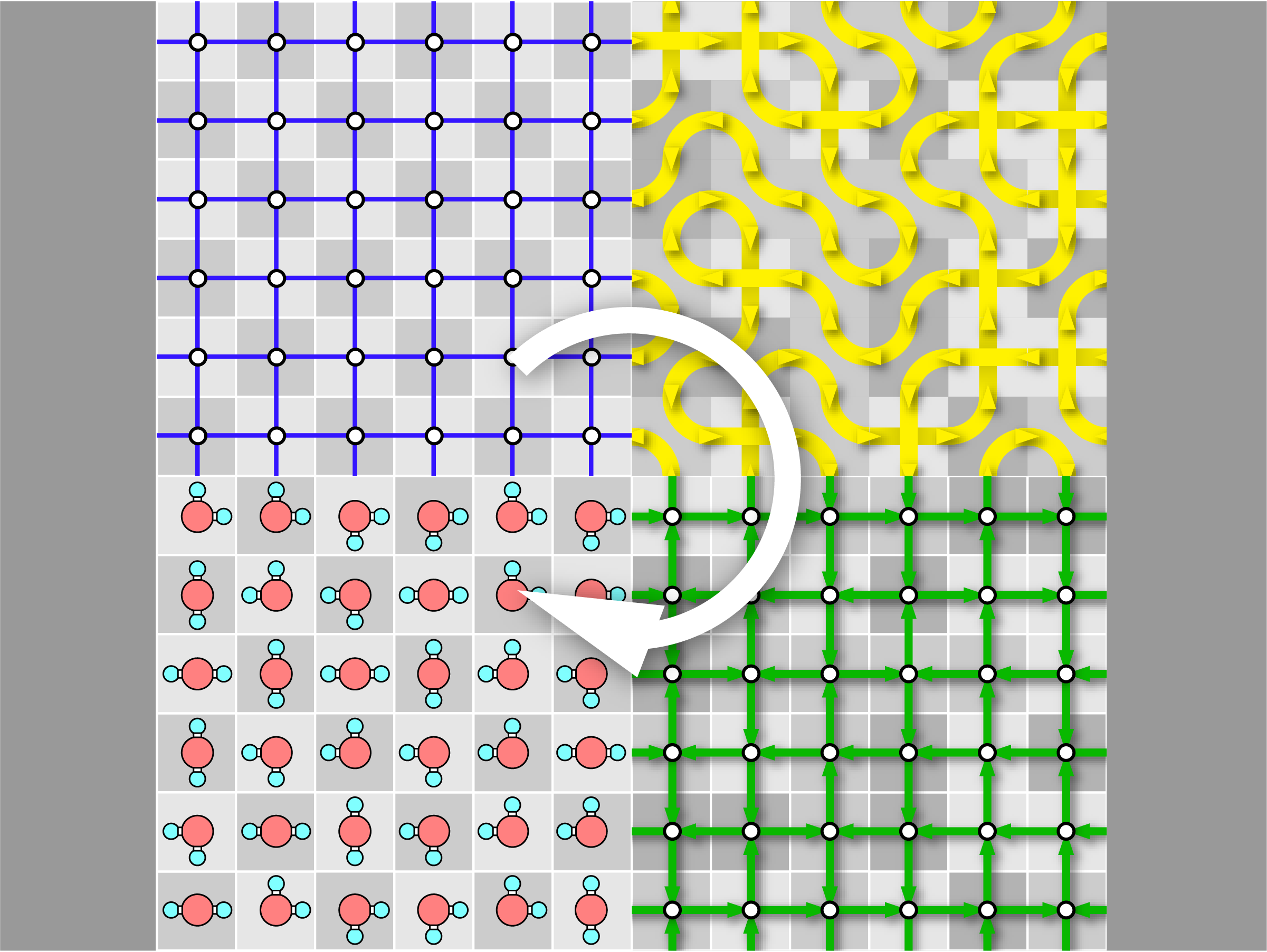
GenIce-core:Efficient Algorithm for Generation of Hydrogen-Disordered Ice Structures
A new paper from our research group has been published. Ice is different from ordinary crystals because it contains randomness, which means that statistical treatment based on ensemble averaging is essential. Ice structures are constrained by topological rules known as the ice rules, which give them unique anomalous properties. These properties become more apparent when the system size is large. For this reason, there is a need to produce a large number of sufficiently large crystals that are homogeneously random and satisfy the ice rules.
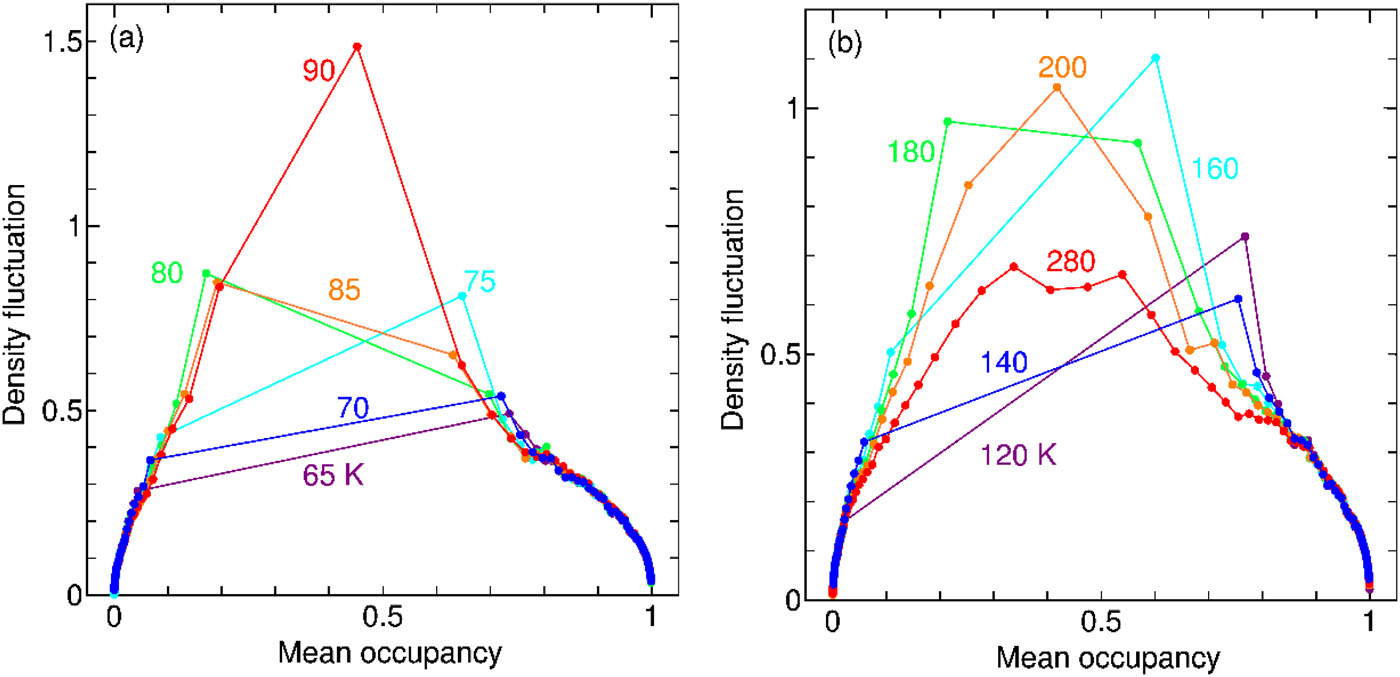
Cage occupancies of CH4, CO2, and Xe hydrates:Mean field theory and grandcanonical Monte Carlo simulations
A new paper from our research group has been published. We propose a statistical mechanical theory for the thermodynamic stability of clathrate hydrates, considering the influence of the guest–guest interaction on the occupancies of the cages. A mean field approximation is developed to examine the magnitude of the influence. Our new method works remarkably well, which is manifested by two sorts of grandcanonical Monte Carlo (GCMC) simulations. One is full GCMC, and the other is designed in the present study for clathrate hydrates, called lattice-GCMC, in which each guest can be adsorbed at one of the centers of the cage.
